COVID-19 is currently the most debated topic . Here is a short glossary of terms related with COVID-19 Which can be asked in competitive exams .
-The Coronavirus-
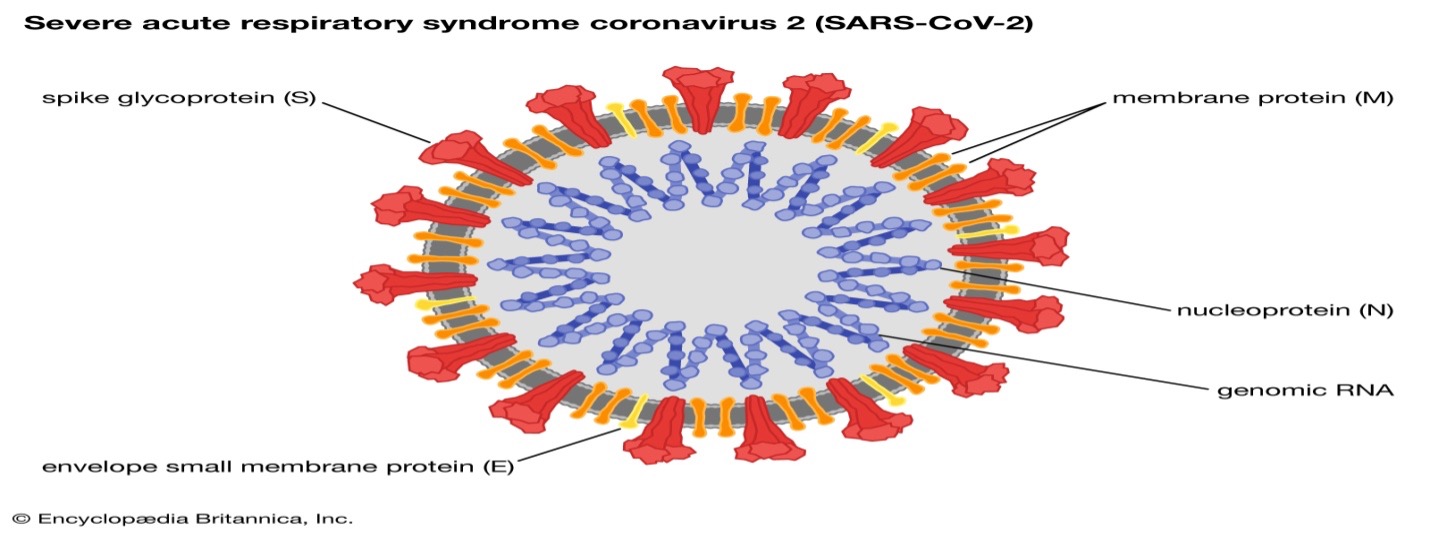
A family of viruses, seven of which are known to the people. They get their name from the crown-like spikes—coronas—that appear on the viruses under a microscope.
Coronaviruses can cause the common cold (which can also be caused by other viruses, such as rhinoviruses), as well as dangerous illnesses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
-Epidemic — When the incidence of a disease rises above the expected level in a particular community or geographic area, it is called an epidemic .
-Pandemic — A global epidemic. When the epidemic spreads over several countries or continents, it is termed a pandemic.
On January 30, WHO announced that COVID-19 was a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
On March 11, WHO decided to announce COVID-19 as a pandemic.
-Percent positive/ positivity rate-
The percent positive is the percentage of all coronavirus tests performed that are actually positive, or: (positive tests)/(total tests) x 100
World Health Organization recommended that the percent positive remain below 5% for at least two weeks before governments consider reopening.
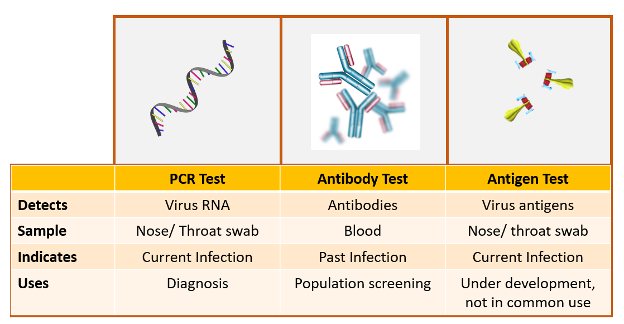
-Antigen Test / Rapid diagnostic tests (RDT),
Antigen tests detect the presence of viral proteins and are used in acute or early infection as the antigen is detected when the virus is actively replicating.
Positive results are highly accurate.
Negative results do not rule out infection and may necessitate confirmation with a molecular test prior to making treatment decisions.
-Antibody Test
An antibody test will indicate whether an individual had a previous infection even if the individual was asymptomatic.
The test does not indicate if an individual has a current infection and shouldn’t be used to diagnose COVID-19 infection.
-RT- PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) — It is the primary test to detect COVID-19 infection across the globe.
It is a sensitive test that uses swab samples drawn from the nasal/oral cavity to test for the presence of viral RNA (ribonucleic acid).
In this test a CT value above 35 means Covid –ve ,Below 35 means Covid positive .
-Cytokine Storm: Is an acute inflammatory syndrome, or an excessive immune response, characterized by fever and multiple organ dysfunction that often develops after a severe viral infection.
A few COVID-19 patients may experience a cytokine storm which could explain the development of critical illness in some patients.
-Reproductive rate (R0): “R zero” or “R naught” refers to the average number of people that an individual with a virus can infect in a completely susceptible .
Scientists believe the R0 for COVID-19 falls between two and three .
-Viral load: measurement of the amount or concentration of a virus in a standard volume of blood, plasma, saliva, mucous, or other bodily fluid; usually expressed as the number of virus particles per milliliter.
-Viral shedding: occurs when a virus replicates inside an organism and is released into the environment.
In COVID-19, it is suspected that SARS-CoV-2 is most contagious when symptoms are worse and viral shedding is high
-Co-morbidities — Several health conditions including uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension, cancer, morbid obesity, lung diseases, compromised immune systems put patients at greater risk for contracting the infection, and also have poor clinical outcomes. Special attention to prevent the disease and prevent mortality in these groups is the concern of health managers.
-Super spreader — Some individuals seem to have the capacity to cause more infections in a disproportionately large number of people, than others. The current pandemic has recorded some super spreaders who have had a huge role in the transmission.
-Infection fatality rate — It is the number of deaths occurring in all infected people in a particular population.
This includes those who might have the COVID-19 infection, but have not been tested for it.
-Case fatality rate — This is the number of deaths occurring among confirmed cases of COVID-19. Since these two figures are available with a certain amount of reliability, it is actually CFR that is being referred to when there is a loose reference to fatality rate.
-Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) — A respiratory disease also caused by a coronavirus, and spread through the same transmission method, i.e. respiratory droplets. The symptoms (fever, cough, body ache, difficulty in breathing) are also similar.
Plasma therapy — Researchers are examining the efficacy of using convalescent plasma, that is, using neutralising antibodies from the blood of people who have recovered from the COVID-19 infection to treat patients with COVID-19.
-Flattening the curve — Reducing the number of new COVID-19 cases, day on day.
The idea of flattening the curve is to ensure that the health infrastructure is not overwhelmed by a large number of cases.

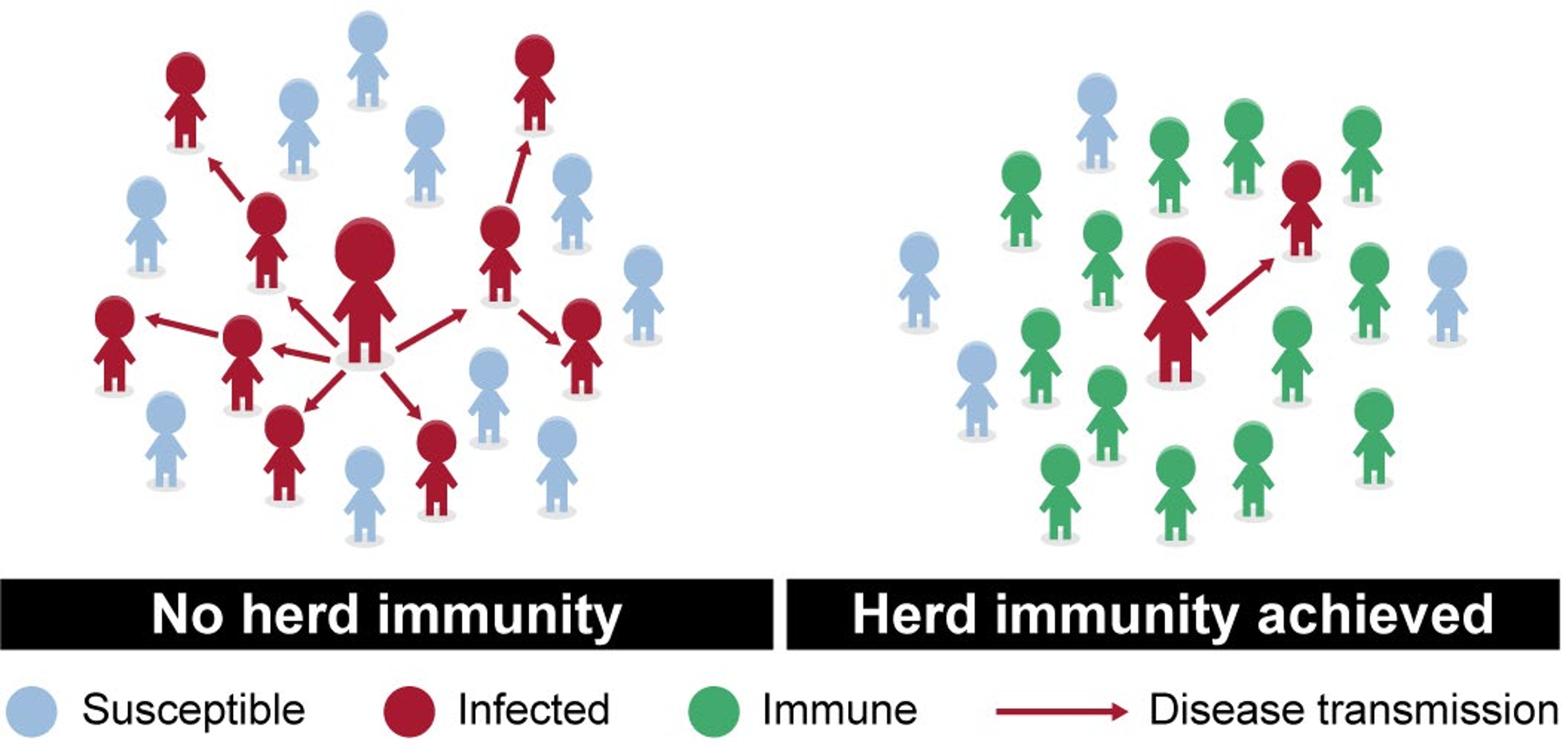
-Herd immunity — This is also known as community immunity, and constitutes the reduction in risk of infection within a population, often because of previous exposure to the virus or vaccination.
- Index case: the first documented case of an infectious disease.
-Index patient: the first person infected with a disease in an epidemic.
Interchangeable with the term “patient zero.”
- Incubation period-
The time between when a person is infected by a virus and when he or she notices symptoms of the disease.
Estimates of the incubation period for COVID-19 range from 2-14 days, but doctors and researchers may adjust that as more data becomes available.




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)




